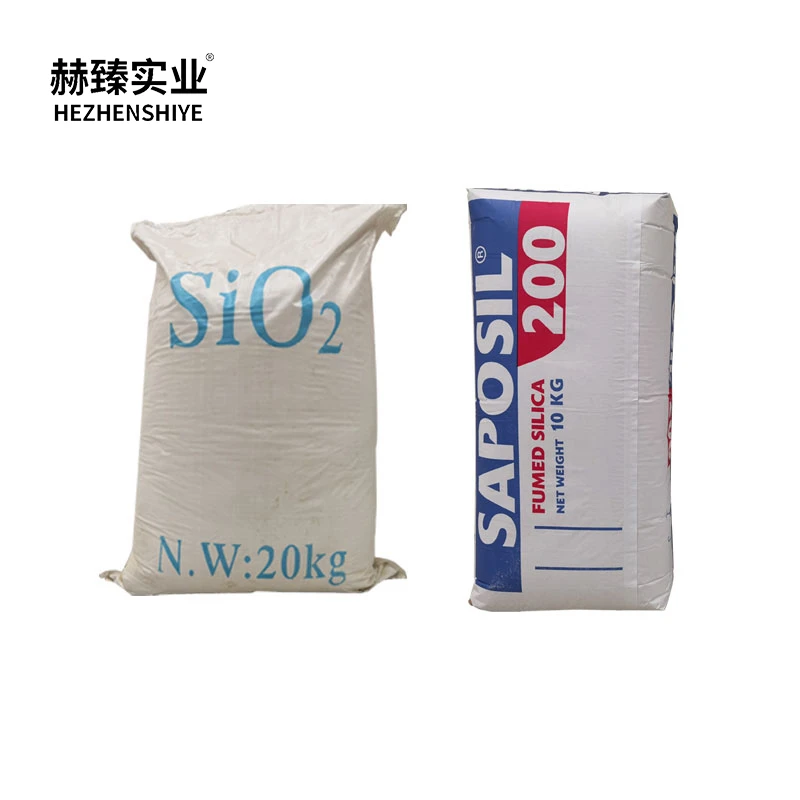
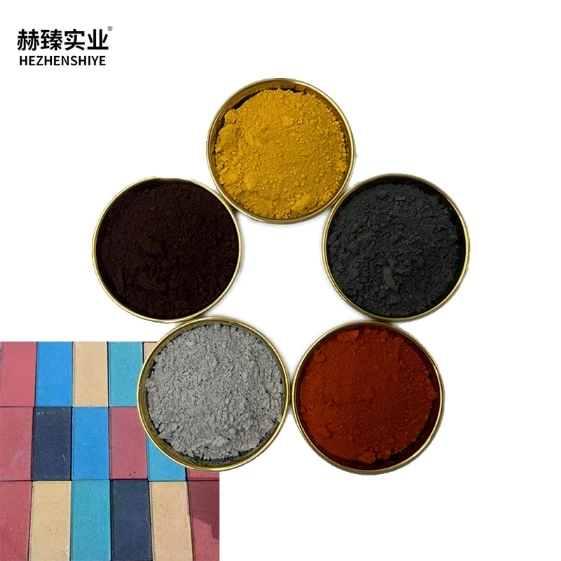
Introducing Calcium Silicon Dioxide, a highly versatile and essential compound used across various industries for its unique combination of chemical properties. Composed of calcium, silicon, and oxygen, Calcium Silicon Dioxide plays a crucial role in materials like refractories, cement, and ceramics, thanks to its ability to enhance strength, durability, and heat resistance. It is particularly valued in the construction and manufacturing sectors for its effectiveness in improving the structural integrity of products exposed to high temperatures and harsh environments. Additionally, Calcium Silicon Dioxide serves as a key additive in the production of steel, where it helps to remove impurities during the refining process, ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product. Its inert nature makes it a safe and reliable option for applications where stability and safety are paramount, such as in the creation of fire-resistant materials. Beyond industrial uses, Calcium Silicon Dioxide is also used in the production of glass, where it enhances transparency, durability, and resistance to thermal shock. As a natural compound, it is non-toxic and environmentally friendly, making it an increasingly popular choice for eco-conscious manufacturers. With its wide range of applications and remarkable performance, Calcium Silicon Dioxide continues to be an indispensable material in industries focused on improving the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of their products. Whether for enhancing construction materials, refining metals, or producing high-performance glass, this compound offers exceptional value and functionality.
Silicon Dioxide Advantages
-
1.Enhance rubber performance+EN SAVOIR PLUSCan significantly improve the tensile strength, tear strength and wear resistance of rubber, improve elasticity and flexibility.
-
2.Reduce rolling resistance+EN SAVOIR PLUSIn tire manufacturing, the use of white carbon black can reduce rolling resistance, improve fuel efficiency and reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
-
3.Improve heat resistance+EN SAVOIR PLUSWhite carbon black has excellent heat resistance, which helps to improve the stability of rubber in high temperature environment.
-
4.Improve the processing performance+EN SAVOIR PLUSIt can improve the processing performance of rubber, such as the fluidity and uniformity in the extrusion and molding process.
-
5.Wide range of applications+EN SAVOIR PLUSNot only suitable for tires, but also widely used in medical rubber, food grade rubber, cable and insulation materials and other special rubber products.
The Versatile Uses of Silicon Dioxide Across Industries
Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), commonly known as silica, is one of the most abundant and versatile compounds in nature, playing a critical role in various industries. Composed of silicon and oxygen, it occurs naturally in materials like sand, quartz, and granite, making it a vital resource for countless applications across different sectors.
One of the most prominent uses of Silicon Dioxide is in the construction industry, where it is a primary component of concrete and cement. Silicon Dioxide enhances the strength and durability of building materials, improving their resistance to weathering and wear. It is also a key ingredient in glass production, where it helps to create clear, transparent glass with high thermal resistance. Silicon Dioxide’s ability to withstand high temperatures makes it ideal for use in refractory materials, which are crucial in industries that involve extreme heat, such as metal smelting, ceramics, and brick manufacturing.
In the electronics industry, Silicon Dioxide plays an essential role in the production of semiconductors and integrated circuits. It is used as an insulating material in microelectronics and as a dielectric layer in capacitors and transistors. Its insulating properties are vital for ensuring the stability and performance of electronic devices.
Silicon Dioxide is also widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. As an anti-caking agent, it prevents clumping in powdered products like spices, powdered drinks, and medications. Additionally, its use in cosmetics helps improve the texture and stability of products like lotions, face powders, and foundations.
Beyond these industrial applications, Silicon Dioxide is an important material in nanotechnology, where it is used to create advanced materials with unique properties for scientific and medical research.
What is Silicon Dioxide? A Comprehensive Overview
Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), commonly known as silica, is a naturally occurring compound composed of silicon and oxygen, two of the most abundant elements in the Earth's crust. It forms a wide variety of minerals, the most common being quartz, which makes up a significant portion of sand, granite, and many other rocks. Silicon Dioxide is a key element in many geological and biological processes, and its versatility makes it an essential substance in numerous industries.
Silicon Dioxide exists in several forms, ranging from crystalline structures like quartz to amorphous forms like glass and diatomaceous earth. Crystalline silica, with its orderly atomic arrangement, is found in materials such as quartz crystals and sand. Amorphous silica, on the other hand, lacks this rigid structure and is found in materials like fumed silica and silica gel.
One of the most important properties of Silicon Dioxide is its high resistance to heat and wear. This makes it an invaluable material in construction, where it is used in the manufacture of concrete, cement, and glass. Its durability also makes it ideal for use in refractories, materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as those used in metal smelting and ceramics production.
Silicon Dioxide also plays a critical role in the electronics industry, where it is used as an insulating material in semiconductors, microchips, and other electronic components. Its electrical insulating properties are essential for ensuring the stability and performance of modern electronic devices.
Additionally, Silicon Dioxide is used in food and pharmaceutical products as an anti-caking agent, as well as in cosmetics and personal care products, where it improves texture and stability.
-
01
-
02
-
03




 Bannière PDF
Bannière PDF Obtenir un devis
Obtenir un devis





