types of silica
2025.01.10
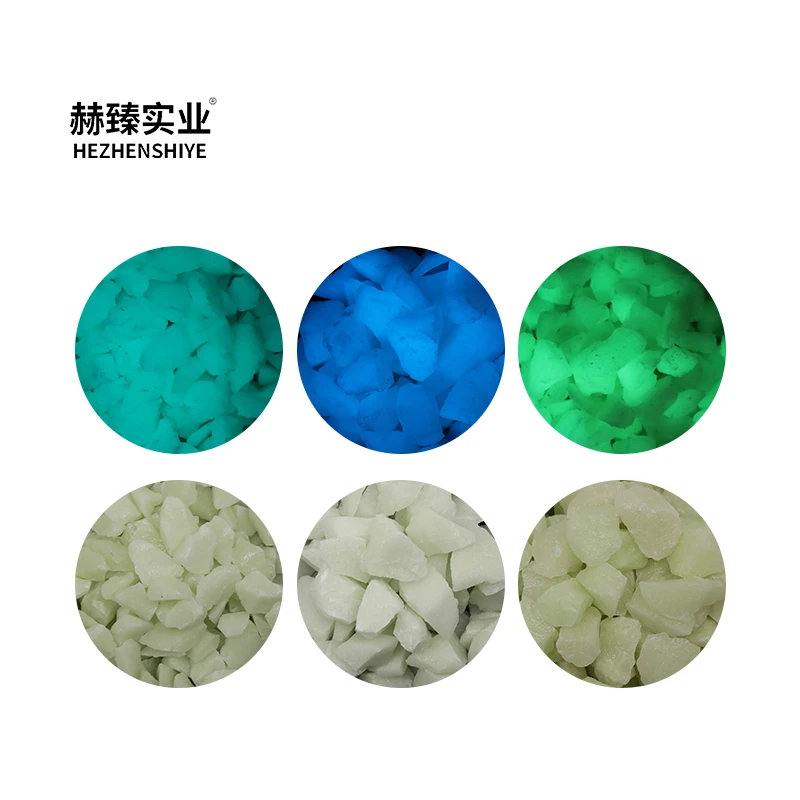
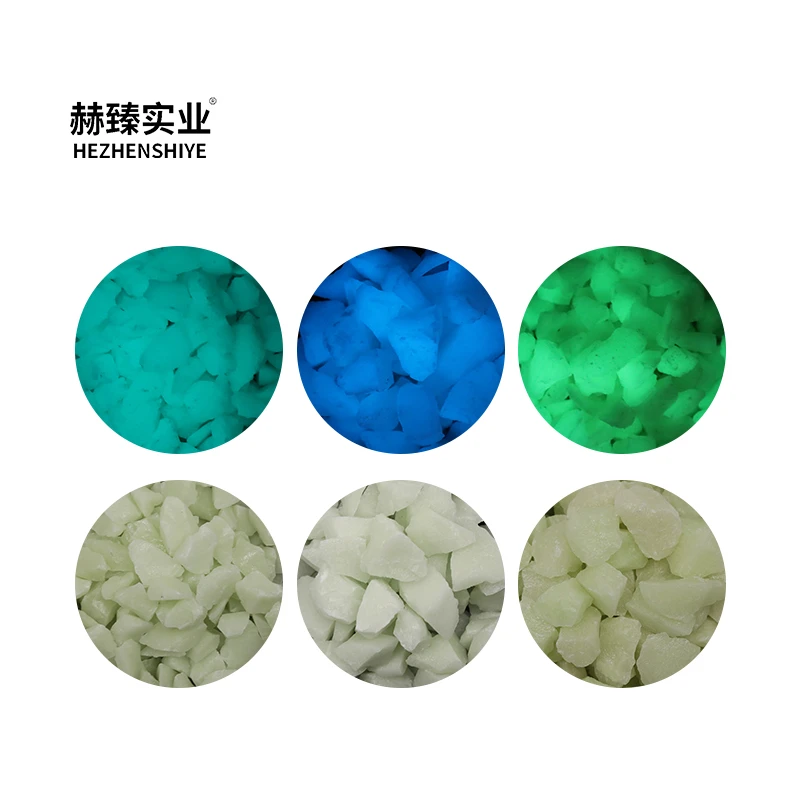
Silica, a versatile mineral, plays an integral role in various industrial applications. Understanding the different types of silica is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their products and processes effectively. Here, we delve into the distinct types of silica, exploring their characteristics and applications to enhance your knowledge and provide a solid foundation for product improvement.
Fumed silica, a synthetic form produced through flame pyrolysis, is renowned for its thickening properties and is a common additive in paints, coatings, and adhesives. It improves the viscosity and stability of liquids, preventing separation and enhancing material performance across various environmental conditions. Beyond the technical aspects, understanding the chemistry of these silica types contributes to formulating innovative solutions tailored to market demands. By leveraging the inherent qualities of each type, businesses can not only improve product quality but also achieve sustainability through efficient resource utilization. Research plays a pivotal role in harnessing the potential of silica variations. Collaborations with scientific institutions can lead to breakthroughs in material science, propelling industries towards more sustainable and efficient practices. This synergy between academia and industry not only drives innovation but also enhances the credibility and authority of businesses in their respective fields. Furthermore, engaging with industry experts, attending seminars, and participating in online forums dedicated to silica advancements can significantly augment a company’s expertise. Such interactions facilitate the exchange of valuable insights and practical experiences, fostering a knowledgeable community around silica applications. In summary, the comprehensive understanding of different types of silica—quartz, cristobalite, and amorphous forms—can catalyze significant advancements and innovations in various sectors. By tapping into extensive research, expert collaborations, and actively engaging with industry networks, companies can gain a competitive edge, ensuring their products not only meet but exceed market expectations. In doing so, they also uphold the principles of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness in the evolving landscape of product development.
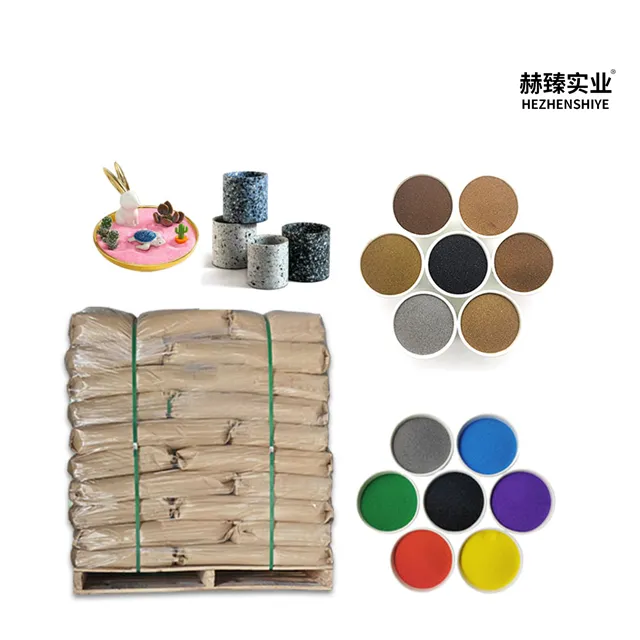


Fumed silica, a synthetic form produced through flame pyrolysis, is renowned for its thickening properties and is a common additive in paints, coatings, and adhesives. It improves the viscosity and stability of liquids, preventing separation and enhancing material performance across various environmental conditions. Beyond the technical aspects, understanding the chemistry of these silica types contributes to formulating innovative solutions tailored to market demands. By leveraging the inherent qualities of each type, businesses can not only improve product quality but also achieve sustainability through efficient resource utilization. Research plays a pivotal role in harnessing the potential of silica variations. Collaborations with scientific institutions can lead to breakthroughs in material science, propelling industries towards more sustainable and efficient practices. This synergy between academia and industry not only drives innovation but also enhances the credibility and authority of businesses in their respective fields. Furthermore, engaging with industry experts, attending seminars, and participating in online forums dedicated to silica advancements can significantly augment a company’s expertise. Such interactions facilitate the exchange of valuable insights and practical experiences, fostering a knowledgeable community around silica applications. In summary, the comprehensive understanding of different types of silica—quartz, cristobalite, and amorphous forms—can catalyze significant advancements and innovations in various sectors. By tapping into extensive research, expert collaborations, and actively engaging with industry networks, companies can gain a competitive edge, ensuring their products not only meet but exceed market expectations. In doing so, they also uphold the principles of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness in the evolving landscape of product development.
Pervious
Next