Silicon dioxide, often a subject of curiosity in the scientific and industrial worlds, plays a crucial role in numerous applications. From its fundamental nature to its diverse uses, understanding silicon dioxide is key to appreciating its significance. Let's explore various aspects related to this compound, including what it is, its applications, and its different forms such as white carbon black and fumed silica.

Silicon Dioxide: What Is It?
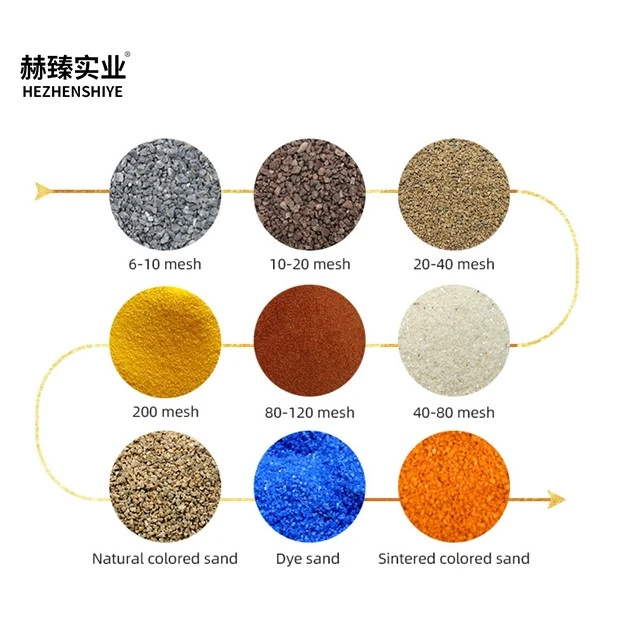
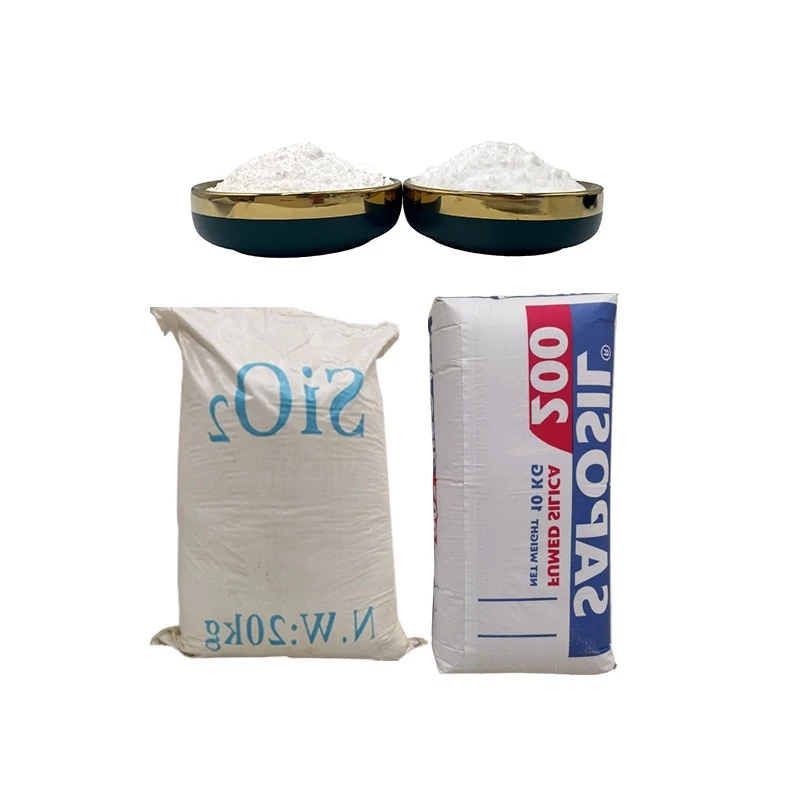
Silicon dioxide what is it is a question frequently asked by those delving into the world of chemistry and materials. Chemically represented as SiO₂, silicon dioxide is one of the most abundant compounds on Earth. It commonly occurs in nature as quartz, which is a major component of sand, granite, and other rocks. In its pure form, silicon dioxide is a hard, brittle, colorless solid with a high melting point. Structurally, it consists of silicon atoms covalently bonded to oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement, forming a three - dimensional network. This unique structure gives it various physical and chemical properties that make it useful in different fields. Whether in the form of crystals or amorphous powders, silicon dioxide's properties make it a material of great interest.
What Is Silicon Dioxide Used For?
The question ثاني أكسيد السيليكون what is it used for has a wide - ranging answer. In the construction industry, silicon dioxide in the form of sand is a primary ingredient in concrete, providing strength and stability. It's also used in the production of glass, where its high melting point and ability to form a transparent solid make it ideal for creating windows, bottles, and optical fibers. In electronics, silicon dioxide is crucial. It serves as an insulator in integrated circuits, protecting the delicate electronic components and preventing unwanted electrical conduction. Additionally, it's used in the manufacturing of semiconductors, where it helps in the formation of thin films and layers. In the food industry, silicon dioxide is used as an anti - caking agent to prevent powdered foods like spices, milk powder, and coffee creamer from clumping together.
The Diverse Uses of SiO₂
SiO₂ use extends far beyond the common applications mentioned above. In the pharmaceutical industry, silicon dioxide is used as a glidant in tablet formulations. It helps improve the flow properties of the powder mixture, ensuring uniform tablet compression. In the cosmetics industry, it's used in products such as face powders and eyeshadows to control texture, absorb moisture, and enhance the product's durability. Silicon dioxide is also used in the production of ceramics, where it contributes to the hardness, strength, and heat resistance of the final product. In the rubber industry, it acts as a reinforcing filler, improving the mechanical properties of rubber compounds, making them more resistant to wear and tear.

White Carbon Black: A Special Form of Silicon Dioxide
White carbon black is a form of silicon dioxide that has unique properties and applications. Also known as precipitated silica, it is produced synthetically rather than mined like natural quartz. It has a high surface area and excellent reinforcing properties, making it a popular additive in the rubber industry, especially for tires. In tires, white carbon black improves traction, reduces rolling resistance, and enhances durability. It's also used in the production of adhesives, sealants, and coatings, where it provides thickening, anti - settling, and reinforcing effects. In the food industry, white carbon black can be used as a flow agent and anti - caking agent, similar to other forms of silicon dioxide, but its fine particle size and high surface area give it additional functionality.
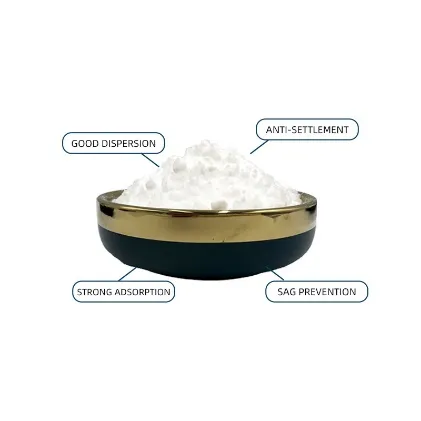
Fumed Silica: A Versatile Silicon Dioxide Variant
Fumed silica is another important form of silicon dioxide. It is produced by the high - temperature hydrolysis of silicon tetrachloride. Fumed silica has extremely fine particles and a high surface area, which gives it excellent thickening, anti - settling, and rheological control properties. In the paint and coating industry, it is used to prevent pigment settling, improve the flow and leveling of the paint, and enhance the scratch resistance of the coated surface. In the epoxy and resin industry, fumed silica is added to improve the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance of the cured products. It's also used in adhesives, where it helps in controlling the viscosity and improving the bonding strength.
Silicon Dioxide FAQs
Is silicon dioxide harmful to humans?
In its natural forms like quartz sand, silicon dioxide is generally considered safe when not inhaled in large quantities. However, respirable crystalline silica dust, which can be generated during activities like sandblasting or stone cutting, is a known human carcinogen. Inhalation of this dust over time can lead to serious lung diseases such as silicosis. On the other hand, the silicon dioxide used in food additives and cosmetics is typically in forms that are not harmful when used as directed.
How is white carbon black different from regular silicon dioxide?
White carbon black, or precipitated silica, is synthetically produced, whereas regular silicon dioxide can be mined from natural sources. White carbon black has a higher surface area and more uniform particle size compared to many natural forms of silicon dioxide. These properties make it more effective as a reinforcing filler in rubber and other applications where specific surface - related functions are required.
Can fumed silica be used in food products?
Fumed silica is not typically used in food products. While silicon dioxide in general can be used as a food additive, fumed silica is mainly used in industrial applications due to its unique physical properties that are more suited for enhancing the performance of paints, coatings, adhesives, and other industrial materials rather than for food - related purposes.
What are the main factors affecting the use of silicon dioxide in different industries?
The main factors include the form of silicon dioxide (such as its particle size, surface area, and structure), its purity, and its cost. Different industries have specific requirements for these properties. For example, in the electronics industry, high purity and precise control over the structure are crucial, while in the construction industry, cost - effectiveness and availability in large quantities are more important considerations.
How is silicon dioxide extracted from natural sources?
When extracting silicon dioxide from natural sources like quartz - rich rocks, the process usually involves crushing and grinding the rocks to reduce their size. Then, through processes such as washing, screening, and magnetic separation, impurities are removed to obtain a relatively pure form of silicon dioxide. In some cases, chemical processes may also be used to further purify the silicon dioxide, depending on the required quality for specific applications.