Volcanic stones mysterious origins from fiery eruptions and diverse applications in modern architecture art environmental protection geological research cultural heritage and material science
2025.11.10
The Birth of Volcanic Stones: A Fiery Genesis
Deep within the Earth's mantle, a seething cauldron of molten rock exists, known as magma. This magma is a complex mixture of various substances, including silicates, gases, and minerals. When the delicate balance of forces within the Earth is disrupted, perhaps due to the movement of tectonic plates or a sudden shift in the Earth's crust, this magma is propelled towards the surface.
As the magma ascends through the Earth's crust, it encounters cooler temperatures and lower pressures. These changing conditions cause the dissolved gases within the magma, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide, to expand rapidly. The expanding gases create a powerful force, like a coiled spring ready to release, that pushes the magma towards the surface with increasing urgency.
When the magma finally breaches the Earth's surface, a volcanic eruption occurs. It's a spectacular and awe - inspiring event. Molten lava, glowing bright orange and red, spills out of the volcano, flowing down its slopes like a river of fire. Some eruptions are more explosive, ejecting large amounts of magma, ash, and rocks high into the air.
Once the magma is exposed to the relatively cold air and water on the Earth's surface, it begins to cool rapidly. This rapid cooling is a crucial step in the formation of volcanic stones. The outer layer of the lava cools first, solidifying into a crust. As the cooling continues, the interior of the lava also solidifies, but the process is not without its complexities.
The rapid cooling of the lava traps the gases that were once dissolved in the magma. These gases, unable to escape completely, form bubbles within the solidifying rock. As the lava continues to cool and harden, these bubbles are preserved, giving volcanic stones their characteristic porous structure. The presence of these pores makes volcanic stones lightweight compared to many other types of rocks. For example, a piece of volcanic stone might feel much lighter in your hand than a similarly sized piece of granite or limestone.
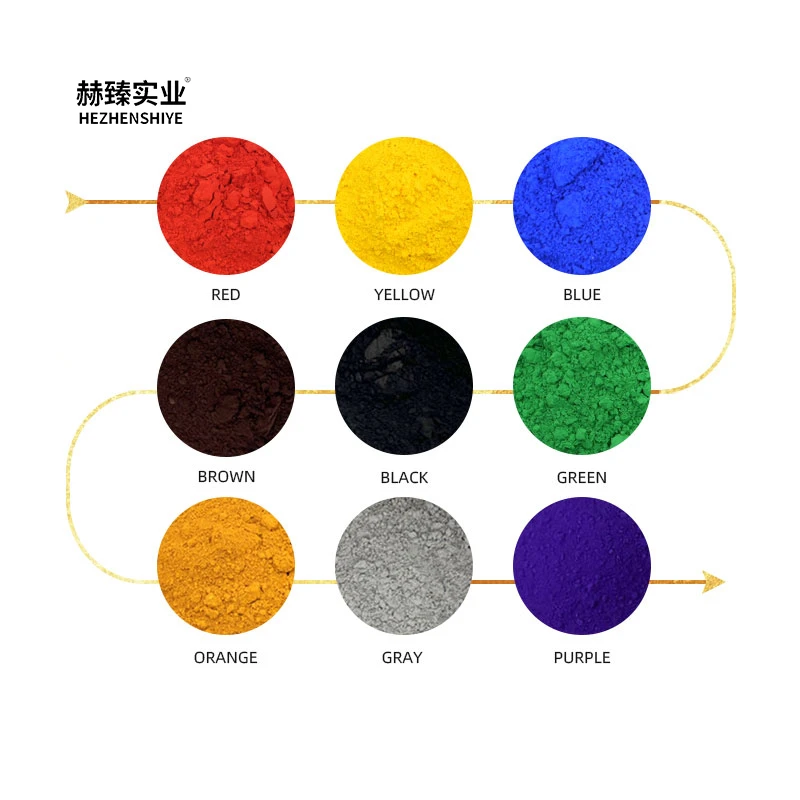
The chemical composition of the magma also plays a significant role in determining the properties of the resulting volcanic stones. Different magmas contain varying amounts of minerals such as feldspar, quartz, and mica. These minerals crystallize as the magma cools, contributing to the unique texture and appearance of the volcanic stones. Some volcanic stones may have a fine - grained texture, while others may have larger crystals, depending on the rate of cooling and the specific mineral composition of the magma.
In addition to the cooling process and chemical composition, the environment in which the lava cools can also influence the formation of volcanic stones. If the lava cools in water, for instance, it may form a type of volcanic rock called pillow lava. The water rapidly cools the outer surface of the lava, causing it to form rounded, pillow - like shapes as it continues to flow. On the other hand, if the lava cools in the open air, it may form more irregularly shaped volcanic stones with a rough, porous surface.
Volcanic Stones in Geological History: Silent Witnesses of Earth's Transformations
Volcanic stones are far more than just rocks scattered across the Earth's surface; they are time - capsules, preserving the secrets of the planet's past. They offer a unique window into the dynamic and ever - changing nature of our planet, providing invaluable insights into the processes that have shaped the Earth over billions of years.
One of the key ways volcanic stones contribute to geological research is by helping scientists understand plate tectonics. The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several large plates that are constantly in motion. Volcanic activity often occurs at the boundaries of these plates. For example, at convergent plate boundaries, where one plate is forced beneath another in a process called subduction, the subducted plate melts as it descends into the hot mantle. This molten material then rises back to the surface, creating volcanic eruptions. The volcanic stones formed from this magma carry chemical signatures that can reveal information about the composition of the subducted plate and the conditions in the mantle.
At divergent plate boundaries, such as the Mid - Atlantic Ridge, plates are moving apart. Magma wells up from the mantle to fill the gap, creating new oceanic crust. The volcanic stones in these areas are rich in minerals that have been brought up from deep within the Earth. By analyzing these stones, geologists can study the processes occurring in the mantle and how they contribute to the formation of new crust.
Volcanic stones also serve as a record of past volcanic eruptions. Each eruption leaves behind a unique layer of volcanic deposits, including lava flows, ash, and pyroclastic materials. These deposits can be dated using various techniques, such as radiometric dating. By studying the sequence of these layers, scientists can reconstruct the history of volcanic activity in a particular area. They can determine the frequency of eruptions, the intensity of each eruption, and how the volcanic activity has changed over time.
The study of volcanic stones in the context of volcanic history has been particularly illuminating in areas like the Yellowstone Caldera in the United States. The Yellowstone region has experienced numerous volcanic eruptions over the past few million years. The volcanic stones found there, including layers of ash and lava, have allowed scientists to piece together a detailed picture of these eruptions. They have discovered that some of these eruptions were extremely large, ejecting massive amounts of volcanic material into the atmosphere and having a significant impact on the global climate at the time.
In addition to plate tectonics and volcanic history, volcanic stones can also provide information about the Earth's ancient climate. The chemical composition of volcanic stones can be influenced by the environmental conditions at the time of their formation. For example, the presence of certain isotopes in volcanic stones can indicate the temperature and humidity of the atmosphere during the volcanic eruption. By analyzing these isotopes in volcanic stones from different periods in the Earth's history, scientists can gain a better understanding of how the climate has changed over time.
Take the case of the Deccan Traps in India. These are a large igneous province formed by extensive volcanic eruptions around 66 million years ago. The volcanic stones in the Deccan Traps have been studied extensively, and they have provided important clues about the environmental changes that occurred during that time. Some scientists believe that the massive volcanic eruptions that formed the Deccan Traps may have contributed to the mass extinction event that led to the disappearance of the dinosaurs. The volcanic emissions could have released large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing significant climate change and disrupting ecosystems around the world.
Another example is the study of volcanic stones in the Antarctic. Volcanic activity has occurred in Antarctica over millions of years, and the volcanic stones found there have been used to study the past climate of the region. Since Antarctica is a sensitive indicator of global climate change, understanding its past climate can help us better predict future changes. The volcanic stones in Antarctica can provide information about factors such as sea - ice extent, temperature, and precipitation in the past, which is crucial for climate research.
Volcanic stones in the geological history are like a complex puzzle, with each piece contributing to our understanding of the Earth's past. Whether it's through revealing the secrets of plate tectonics, reconstructing the history of volcanic eruptions, or providing insights into ancient climates, these silent witnesses of Earth's transformations continue to play a vital role in modern geological research.
Volcanic Stones in Cultural and Historical Contexts: Symbols of the Ancients
Volcanic stones have long held a special place in the cultural and historical tapestries of human civilizations around the world. Their unique origin and properties have made them not just materials for practical use but also powerful symbols laden with meaning.
In the mysterious Easter Island, volcanic stones are the medium through which the island's ancient inhabitants left behind a legacy that continues to baffle and intrigue the modern world. The large - headed statues carved from volcanic rock, known as Moai, are iconic. These colossal figures, some towering over 10 meters tall, were crafted from the volcanic tuff found on the island. The process of carving these statues must have been labor - intensive, involving the use of stone tools to shape the hard volcanic material. Each Moai has a distinct facial expression, with deep - set eyes, prominent noses, and solemn countenances. They were likely symbols of important ancestors or deities in the Rapa Nui culture. Standing in rows, they seem to be guardians, watching over the island, its people, and its history.
Moreover, some of the volcanic stones on Easter Island were inscribed with hieroglyphic tablets. These inscriptions, though not fully deciphered, are believed to contain important information about the island's history, religious beliefs, and social structure. The use of volcanic stones for such inscriptions indicates the significance placed on these stones in the cultural and communicative practices of the ancient Rapa Nui people. It was as if they recognized the durability of volcanic stones and chose them to preserve their knowledge and stories for future generations.
In ancient Mesoamerican civilizations, volcanic stones, particularly obsidian, were highly valued resources. Obsidian, a type of volcanic glass, was prized for its sharp edges and strength. The Maya, Aztec, and Zapotec civilizations, among others, made extensive use of obsidian. They crafted it into a variety of tools, such as knives, arrowheads, and scrapers. These obsidian tools were far more efficient than those made from other materials available at the time. For example, obsidian knives could make cleaner cuts, whether in hunting, processing food, or working with materials like wood and leather.
Obsidian also had a significant role in religious and ceremonial contexts. In the Aztec Empire, green obsidian from the Pachuca Mountains was especially revered. It was used to create ceremonial objects such as jewelry, miniature weapons, and sculptures. These items were often buried as offerings in temples, like the Templo Mayor in Tenochtitlan. The choice of obsidian for these religious artifacts was not arbitrary. Its unique sheen and the difficulty in obtaining it from specific regions made it a symbol of power, divinity, and the sacred.
In the Zapotec civilization, obsidian was also a crucial part of their trade network. They sourced obsidian from different regions and traded it with other cultures. This trade not only facilitated the exchange of goods but also the spread of ideas and cultural practices. The movement of obsidian across Mesoamerica was a testament to the economic and cultural interconnectedness of the ancient civilizations in the region.
Volcanic stones have also been used in construction and art in various other cultures. In some ancient cultures, volcanic stones were used to build temples and monuments. The solidity and durability of volcanic stones made them ideal for constructing structures that were meant to last. These buildings often served as centers of religious worship, political power, or community gatherings. The use of volcanic stones in their construction added to the grandeur and permanence of these structures.
In art, volcanic stones have been carved into intricate sculptures, not just in Easter Island and Mesoamerica but in many other parts of the world. Artists have been drawn to the unique texture and color variations of volcanic stones. Whether it's the rough - hewn simplicity of some primitive sculptures or the highly detailed and sophisticated works of more advanced art traditions, volcanic stones have provided a medium for creative expression. These sculptures often represent aspects of the culture's mythology, daily life, or spiritual beliefs.
Volcanic Stones in Modern Architectural Marvels: A Blend of Aesthetics and Durability
In the realm of modern architecture, volcanic stones have emerged as a favored choice for architects and designers, offering a harmonious blend of aesthetics and durability. Their unique characteristics make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from flooring to decorative accents, adding a touch of natural elegance to any structure.
One of the most common uses of volcanic stones in modern architecture is for flooring. The rough, textured surface of volcanic stones provides excellent traction, making them a safe choice for both indoor and outdoor areas. In commercial buildings such as hotels and shopping malls, volcanic stone floors can create a sense of grandeur and sophistication. For example, in a luxury hotel lobby, large - format volcanic stone tiles can be used to cover the floor. The natural variations in color and texture of the stones add an organic and earthy element to the otherwise sleek and modern space. The different shades of gray, black, or even reddish - brown in the volcanic stones can create a visually interesting pattern, drawing the eye and creating a focal point.
In residential settings, volcanic stone flooring can transform a simple living room or patio into a cozy and inviting space. The stones' natural warmth and rustic charm make them a great fit for homes with a more traditional or natural - inspired decor. A homeowner might choose to install volcanic stone tiles in a farmhouse - style kitchen, where the stones' rough texture complements the wooden cabinets and exposed beams, creating a charming and down - to - earth atmosphere.
Volcanic stones are also highly valued for their use in decorative elements within buildings. They can be used to create stunning feature walls that serve as the centerpiece of a room. In a contemporary office building, a volcanic stone accent wall in the reception area can make a strong visual statement. The irregular shapes and textures of the stones give the wall a three - dimensional quality, adding depth and interest to the otherwise plain space. The wall can be lit strategically with recessed lights or spotlights, highlighting the natural beauty of the volcanic stones and creating a dramatic effect.
Another innovative use of volcanic stones in modern architecture is in the design of indoor and outdoor pools. The natural non - slip property of volcanic stones makes them an ideal choice for pool surrounds. A resort might line its infinity pool with volcanic stones, creating a seamless transition between the pool and the surrounding landscape. The stones' dark colors, often a rich charcoal or deep black, can enhance the visual impact of the pool, making the water appear even more inviting and the overall setting more luxurious.
For the interior surfaces of pools, volcanic stones can be used to create a unique and natural - looking finish. The porous nature of the stones allows for better water circulation and filtration, which can contribute to the overall health and cleanliness of the pool. Additionally, the rough texture of the stones provides a natural grip, reducing the risk of slips and falls, even when the surface is wet. This makes volcanic stones a practical and stylish choice for pool owners who want to combine functionality with aesthetics.
In addition to flooring and decorative elements, volcanic stones can also be incorporated into the structural elements of a building. Their high strength and durability make them suitable for use in load - bearing walls and columns. In some modern eco - friendly buildings, volcanic stones are used as part of a sustainable construction approach. The stones' natural insulation properties can help to reduce energy consumption by keeping the interior of the building warm in winter and cool in summer. This not only contributes to a more comfortable living or working environment but also aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable and energy - efficient architecture.
The use of volcanic stones in modern architecture is not just about their physical properties but also about the emotional and cultural resonance they bring. Their connection to the earth and the powerful forces of nature that created them can evoke a sense of wonder and a deeper appreciation for the natural world. Whether it's a large - scale commercial development or a small - scale residential project, volcanic stones have the potential to transform a building into a work of art, combining form and function in a way that is both timeless and contemporary.
Volcanic Stones in the Realm of Art: Sculptures Carved from the Earth's Fury
The raw, untamed beauty of volcanic stones has long lured artists into its creative embrace, serving as a canvas for their most profound expressions. These stones, born from the intense forces of the Earth's interior, offer a unique medium that combines durability with a natural aesthetic, making them ideal for sculptural endeavors.
Artists are first drawn to the texture of volcanic stones. The rough, porous surface of these stones provides a tactile quality that is both earthy and primal. When an artist runs their hand over a piece of volcanic stone, they can feel the history and the power of the volcanic eruption that formed it. This texture can be used to great effect in sculptures. For example, in a large - scale abstract sculpture, the rough texture of the volcanic stone can create a sense of movement and energy. The irregularities in the surface can catch the light in different ways, creating a play of shadows and highlights that gives the sculpture a dynamic and three - dimensional appearance.
The color palette of volcanic stones is another source of inspiration. Ranging from deep blacks and grays to warm browns and reds, these natural hues can evoke a wide range of emotions and themes. A black volcanic stone might be used to create a solemn and mysterious sculpture, perhaps representing the depths of the Earth or the unknown mysteries of the universe. On the other hand, a red - hued volcanic stone could be crafted into a sculpture that symbolizes passion, energy, or the life - giving force of the Earth. The natural colors of the stones eliminate the need for artificial pigments in many cases, allowing the true essence of the material to shine through.
One of the challenges and joys of working with volcanic stones is the carving process. Due to their hardness and unique structure, carving volcanic stones requires patience, skill, and the right tools. Traditional stone - carving tools such as chisels and hammers are often used, but modern artists may also incorporate power tools to speed up the process while still maintaining precision. The act of carving into the volcanic stone is a slow and meditative one. The artist must carefully remove layers of the stone, revealing the form hidden within. Each strike of the chisel is a decision, a step towards bringing the vision to life.
In contemporary art, volcanic stones have found their way into a variety of sculptural styles. In minimalist sculptures, the simplicity of the form is enhanced by the natural texture and color of the volcanic stone. A simple, smooth - sided cube carved from volcanic stone can be a study in contrasts, with the rough stone surface against the clean geometric shape. This creates a visual tension that draws the viewer in, making them contemplate the relationship between nature and human - made form.
In more organic and figurative sculptures, volcanic stones can be shaped to represent the human form, animals, or elements of the natural world. An artist might carve a life - sized statue of a bird from volcanic stone, using the stone's texture to mimic the feathers and its color to bring out the details of the bird's plumage. The weight and density of the volcanic stone give the sculpture a sense of solidity and permanence, as if it has been rooted in the Earth for centuries.
Volcanic stones also play a role in public art installations. In urban settings, large - scale sculptures made from volcanic stones can become focal points, adding a touch of nature and history to the cityscape. A public park might feature a series of interconnected volcanic stone sculptures that form a walking path or a central gathering area. These sculptures not only beautify the space but also engage the public, inviting them to interact with the art and learn about the unique properties of volcanic stones.
Moreover, the use of volcanic stones in art is not limited to traditional carving techniques. Some artists combine volcanic stones with other materials such as metal, glass, or wood to create mixed - media sculptures. The contrast between the hard, rough volcanic stone and the smooth, shiny surfaces of the other materials can create a visually stunning effect. For instance, a sculpture might feature a volcanic stone base with metal rods or glass panels rising from it, creating a dynamic and contemporary piece that explores the relationship between different materials and textures.
In the world of art, volcanic stones are more than just a medium; they are a source of inspiration, a connection to the Earth, and a testament to the creative spirit of humanity. Whether in a small studio or a large public space, the sculptures created from volcanic stones continue to captivate, inspire, and challenge our perceptions of art and the natural world.
Volcanic Stones in Environmental Protection: Guardians of Water Purity
In the pursuit of a cleaner and healthier environment, volcanic stones have emerged as unsung heroes in the realm of water purification. Their unique physical and chemical properties make them invaluable tools in the fight against water pollution, playing a crucial role in various water treatment processes.
The porous structure of volcanic stones is the key to their effectiveness in water purification. These pores, ranging in size from tiny micropores to larger channels, create a vast surface area within the stones. When water passes through volcanic stones, the pores act like a complex network of traps, effectively intercepting and adsorbing suspended particles, sediment, and organic matter in the water. For example, in a river or lake that has been contaminated by soil erosion, the suspended sediment particles can be trapped by the pores of volcanic stones, preventing them from further polluting the water body.
The surface of volcanic stones also provides a hospitable environment for a diverse community of microorganisms. These microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, form a slimy layer on the surface of the stones, known as a biofilm. The biofilm is a dynamic ecosystem where microorganisms work together to break down organic pollutants in the water. Organic matter such as decaying plants, animal waste, and industrial organic by - products can be decomposed by these microorganisms into simpler, less harmful substances. This biological decomposition process is a natural and sustainable way to purify water, and volcanic stones serve as the perfect substrate for these beneficial microorganisms to thrive.
In municipal wastewater treatment plants, volcanic stones are often used in biological filtration systems. These systems, such as biofilters and constructed wetlands, rely on the combined action of volcanic stones and microorganisms to treat wastewater. The wastewater is passed through a bed of volcanic stones, where the suspended solids are removed by physical filtration, and the organic pollutants are broken down by the microorganisms living on the stones. This treatment process can significantly reduce the levels of chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and nitrogen compounds in the wastewater, making it suitable for safe discharge into the environment or for further reuse.
Industrial wastewater, which often contains a complex mixture of pollutants such as heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and high - strength organic matter, can also be treated using volcanic stones. In some industrial water treatment processes, volcanic stones are used as part of a multi - stage treatment system. They can be used to pre - treat the wastewater by removing large particles and some of the organic matter, reducing the load on subsequent treatment processes. Additionally, the adsorption properties of volcanic stones can help to remove certain heavy metals from the wastewater, although for highly contaminated industrial wastewater, additional treatment methods may be required in combination with volcanic stone filtration.
Volcanic stones are also popular in the world of aquaculture and aquarium keeping. In aquaculture ponds, volcanic stones can be placed at the bottom or used in water circulation systems. They help to maintain water quality by filtering out uneaten fish feed, fish waste, and other organic debris. The porous structure of the stones also provides a habitat for beneficial bacteria that can break down harmful ammonia, which is a common by - product of fish metabolism, into less toxic nitrites and then nitrates. In aquariums, volcanic stones are often used as decorative elements as well as filtration media. They can create a natural - looking environment for fish and other aquatic organisms while also contributing to the overall water quality by adsorbing impurities and providing a surface for beneficial bacteria to grow.
Moreover, in landscape ponds and fountains, volcanic stones can be used to enhance both the aesthetic appeal and the water quality. The stones can be arranged in an artistic manner to create beautiful water features, and at the same time, they act as natural filters, keeping the water clean and clear. The presence of volcanic stones in these water bodies can reduce the need for chemical water treatments, making the environment more eco - friendly.
The use of volcanic stones in water purification is not only effective but also environmentally friendly. As a natural material, volcanic stones are non - toxic and do not introduce harmful chemicals into the water during the treatment process. They are also durable and can be reused for long periods, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste. This makes volcanic stones a sustainable choice for water treatment, aligning with the global trend towards more environmentally conscious and resource - efficient practices.
Future Prospects: Unraveling More Mysteries and Expanding Applications of Volcanic Stones
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the future holds great promise for the study and utilization of volcanic stones. Scientists are constantly exploring new ways to unlock the full potential of these remarkable rocks, and there are several exciting prospects on the horizon.
In the field of materials science, researchers are delving deeper into the unique properties of volcanic stones to develop new and innovative materials. The high strength - to - weight ratio and the natural insulation properties of volcanic stones make them an attractive option for the development of lightweight and energy - efficient building materials. In the coming years, we may see the emergence of new types of volcanic - stone - based composites that combine the best qualities of the stones with other materials such as polymers or metals. These composites could find applications in a wide range of industries, from construction to aerospace, where lightweight and durable materials are highly sought after.
For example, ongoing research is focused on developing volcanic - stone - reinforced polymers. By embedding small particles of volcanic stones into a polymer matrix, scientists aim to enhance the mechanical properties of the polymer, such as its strength and stiffness, while also taking advantage of the natural insulating and fire - resistant properties of the volcanic stones. This could lead to the development of materials that are not only stronger and more durable but also more sustainable, as volcanic stones are a natural and abundant resource.
In environmental protection, the role of volcanic stones in water purification is likely to expand. With the growing global concern over water pollution and the need for clean and safe water sources, the use of volcanic stones in water treatment systems is expected to become more widespread. Scientists are working on optimizing the design of volcanic - stone - based water filters and developing new techniques to improve their efficiency. For instance, they are exploring ways to modify the surface of volcanic stones to increase their adsorption capacity for specific pollutants, such as heavy metals or organic contaminants. This could make volcanic - stone - based water treatment systems even more effective in removing a wider range of pollutants from water, providing a sustainable solution to the global water - quality challenges.
Moreover, volcanic stones may also play a role in the emerging field of carbon capture and storage. Some studies have suggested that certain types of volcanic stones could potentially react with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere or in industrial emissions, trapping the carbon dioxide and converting it into more stable compounds. If further research can validate and optimize this process, volcanic stones could become a valuable tool in the fight against climate change by helping to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
In the cultural and artistic realms, volcanic stones will likely continue to inspire creativity. As more people become aware of the unique beauty and historical significance of volcanic stones, there may be an increased demand for artworks, sculptures, and architectural designs that incorporate these stones. Artists and architects will have the opportunity to experiment with new techniques and forms, pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with volcanic stones. This could lead to the creation of more innovative and thought - provoking works that celebrate the natural world and its geological wonders.
The future of volcanic stones is full of possibilities. Whether it's through advancements in materials science, environmental protection, or creative expression, these remarkable rocks will continue to shape our world in new and unexpected ways. As we continue to explore and understand the mysteries of volcanic stones, we can look forward to a future where their potential is fully realized, bringing benefits to various aspects of our lives and contributing to a more sustainable and creative future.