- Introduction to silica si02
and its significance - Technical attributes and breakthrough advantages
- Comprehensive manufacturer comparison
- Customized solutions tailored to diverse industries
- In-depth application case studies
- Challenges and future developments in silica-based technologies
- Conclusion: The pivotal role of silica si02 in advanced materials

(silica si02)
Understanding Silica Si02: Properties and Modern Relevance
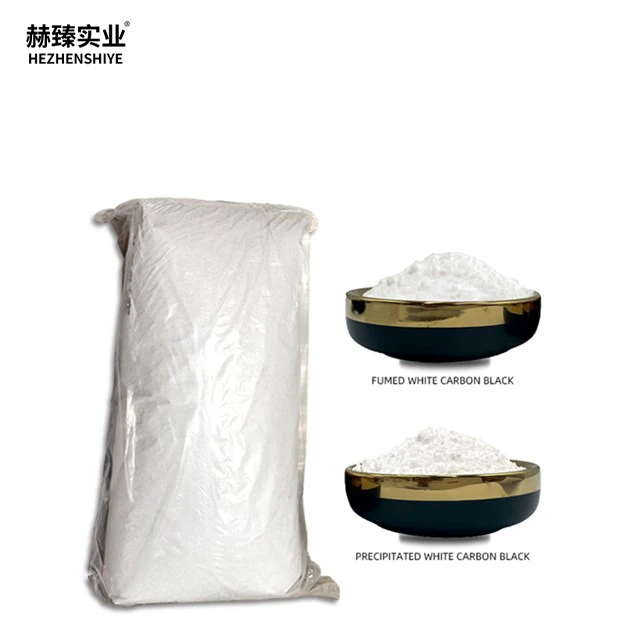
Silica Si02, chemically recognized as silicon dioxide, is among the most abundant compounds in the Earth's crust and an indispensable engineered material across multiple industries. In its most common form, it appears as quartz or amorphous silica, demonstrating remarkable chemical stability and surface versatility. Its global relevance has skyrocketed in the last decade due to advancements in nanotechnology, surface science, and material engineering.
Globally, the silica market was valued at USD 13.58 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 21.42 billion by 2030, registering a robust CAGR of 5.7% (source: Grand View Research, 2023). The demand is fueled by the expanding applications in the construction, automotive, electronics, and renewable energy sectors. Hydrophobic silica and micro silica have gained notable attention for their unique surface modifications and reactivity, enabling high-performance in fields such as sealants, rubber compounding, and high-strength concrete.
Ongoing research continues to unlock new functionalities and cost-effective manufacturing techniques, driving transformative changes and sustainability across global supply chains.
Technical Breakthroughs and Competitive Advantages
The technical evolution of silica Si02 is defined by innovations in purity, morphology control, and surface chemistry. Modern manufacturing yields ultra-fine particles with surface areas exceeding 300 m2/g, offering superior dispersibility and unparalleled interaction in polymer matrices. Hydrophobic silica, engineered via surface functionalization (often with organic silanes), exhibits robust moisture resistance, making it a preferred additive in paints, plastics, and personal care products.
Micro silica, a byproduct from silicon alloy production, displays spherical morphology and extreme fineness (mean diameter of 0.1-0.3 microns), which imparts exceptional pozzolanic activity in high-performance concrete formulations. This translates to increased compressive strength (up to 25% improvement) and enhanced durability. Other critical technical characteristics include controlled particle size distribution, thermal stability above 1,100°C, and tailor-engineered surface energies.
These breakthroughs enable product designers and engineers to solve complex processing challenges, optimize end-use application performance, and meet the stringent requirements of next-generation materials.
Manufacturer Comparison: Key Performance Data
Selecting the appropriate silica supplier is crucial for consistent quality, application-specific performance, and regulatory compliance. The following table compares major manufacturers, focusing on their core product offerings, technical specifications, annual capacity, and compliance standards:
| Manufacturer | Core Product Type | Surface Area (m2/g) | Purity (%) | Hydrophobic Options | Annual Capacity (ktons) | Main Industry Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evonik Industries | Fumed, Precipitated, Hydrophobic | 200–380 | ≥99.8 | Yes (AEROSIL®) | 350 | REACH, FDA |
| PPG Industries | Precipitated, Silicas for Rubber | 120–250 | ≥99.5 | Yes | 200 | REACH |
| Wacker Chemie | Fumed, Specialized (HDK®) | 100–300 | ≥99.7 | Yes | 160 | REACH, ISO 9001/14001 |
| Elkem | Micro Silica (Silica Fume) | 15–25 | ≥92.0 | No | 120 | ISO 9001 |
| Cabot Corporation | Fumed, Hydrophobic | 150–400 | ≥99.8 | Yes (CAB-O-SIL®) | 170 | FDA, REACH |
The selection process must address not only technical fit but also factors such as logistics, after-sales support, and proven track record in application-specific projects.
Customized Solutions for Multifaceted Industrial Needs
Industrial sectors increasingly demand silica-based products engineered to unique use-case requirements. Custom solutions extend from particle size tuning and surface chemistry adaptation to functional group grafting. For instance, pharmaceutical manufacturers may require silica carriers with tightly controlled porosity and bio-inertness, while the elastomer industry values silica with controlled hydroxyl functionalities for optimal reinforcement and rolling resistance.
Hydrophobic silica is customized by selecting specific silane treatments to impart oleophobicity, improving flow properties in powder coatings and cosmetics. Recent industrial collaborations have resulted in proprietary grades with combined characteristics, such as high dispersibility and anti-caking performance, for use in high-throughput food processing or advanced polymer blends.
Design-to-order processes usually involve pilot batch production, rigorous application testing, and real-time process optimization in partnership with both material scientists and end-users.
Application Cases: Silica Si02, Hydrophobic Silica, and Micro Silica
Real-world applications reflect the extensive versatility and value addition provided by silica Si02, hydrophobic silica, and micro silica.
High-performance Rubber Compounds: Integration of precipitated silica enhances abrasion resistance and lowers rolling resistance for green tire applications, leading to up to 30% reduction in fuel consumption.
Concrete and Construction: Micro silica incorporation in concrete mixtures yields compressive strength improvements (from 70 to 90 MPa in bridge decks) and mitigates chloride ingress, critical for marine infrastructures.
Paints and Coatings: Hydrophobic silica acts as a matting agent and rheology modifier, delivering anti-settling and anti-sagging effects in high-performance coatings, especially for automotive refinishes.
Personal Care: In toothpaste formulations, engineered silica acts as a gentle abrasive, balancing cleaning efficiency with enamel preservation, and provides viscosity control in gels.
Electronics and Photovoltaics: Ultra-high purity silica serves as encapsulant filler and substrate in semiconductor fabrication, with defect levels under 3 ppm, dramatically improving yield rates.
Current Challenges and Prospective Developments
Despite significant advancements, silica-based materials confront ongoing challenges in terms of scalability, process economics, and environmental policies. Energy consumption during fumed silica production, for example, remains a concern, prompting a shift toward greener manufacturing protocols and recycling strategies. In the context of micro silica, the emphasis is on minimizing heavy metal impurities and ensuring consistent quality from industrial byproducts.
From a technical perspective, future directions include hierarchical pore structure engineering for enhanced adsorption, hybrid organic-inorganic silica composites, and digital quality tracking using AI-enabled analytics. The roadmap also points to increasing regulatory oversight regarding nanoparticle safety and lifecycle sustainability.
Strategic alliances between suppliers, research institutes, and end-users are central to overcoming market fragmentation and accelerating innovation pipelines in the field of engineered silica.
The Enduring Role of Silica Si02 in Material Innovation
Silica Si02, encompassing both hydrophobic variants and micro silica, has established itself as a backbone of material innovation. Its technical adaptability underpins critical advances in sectors spanning green mobility, infrastructure resilience, digital technology, and sustainable consumer products.
As industries worldwide embrace increasingly stringent performance and sustainability standards, the value proposition offered by tailored silica solutions is projected to expand even further. Ongoing advancements in process efficiency, regulatory alignment, and collaborative research ensure that silica Si02 will remain at the forefront of advanced material science and industrial application for years to come.
Stakeholders committed to next-generation technologies will continue to prioritize strategic partnerships, transparent sourcing, and robust technical support, cementing silica Si02's pivotal role in shaping the future of high-performance materials.

(silica si02)